Hello Programmers/Coders, Today we are going to share solutions of Programming problems of HackerRank of Programming Language SQL. At Each Problem with Successful submission with all Test Cases Passed, you will get an score or marks. And after solving maximum problems, you will be getting stars. This will highlight your profile to the recruiters.
In this post, you will find the solution for Challenges in SQL-HackerRank Problem. We are providing the correct and tested solutions of coding problems present on HackerRank. If you are not able to solve any problem, then you can take help from our Blog/website.
Use “Ctrl+F” To Find Any Questions Answer. & For Mobile User, You Just Need To Click On Three dots In Your Browser & You Will Get A “Find” Option There. Use These Option to Get Any Random Questions Answer.
Introduction To SQL
SQL stands for Structured Query Language. SQL is used to create, remove, alter the database and database objects in a database management system and to store, retrieve, update the data in a database. SQL is a standard language for creating, accessing, manipulating database management system. SQL works for all modern relational database management systems, like SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, etc.
- It is a standard language for Relational Database System. It enables a user to create, read, update and delete relational databases and tables.
- All the RDBMS like MySQL, Informix, Oracle, MS Access and SQL Server use SQL as their standard database language.
- SQL allows users to query the database in a number of ways, using English-like statements.
Link for the Problem – Challenges SQL – Hacker Rank Solution
Challenges SQL – Hacker Rank SolutionProblem:
Julia asked her students to create some coding challenges. Write a query to print the hacker_id, name, and the total number of challenges created by each student. Sort your results by the total number of challenges in descending order. If more than one student created the same number of challenges, then sort the result by hacker_id. If more than one student created the same number of challenges and the count is less than the maximum number of challenges created, then exclude those students from the result.
Input Format
The following tables contain challenge data:
- Hackers: The hacker_id is the id of the hacker, and name is the name of the hacker.

- Challenges: The challenge_id is the id of the challenge, and hacker_id is the id of the student who created the challenge.

Sample Input 0
Hackers Table:  Challenges Table:
Challenges Table: 
Sample Output 0
21283 Angela 6 88255 Patrick 5 96196 Lisa 1
Sample Input 1
Hackers Table:Challenges Table:
Sample Output 1
12299 Rose 6 34856 Angela 6 79345 Frank 4 80491 Patrick 3 81041 Lisa 1
Explanation
For Sample Case 0, we can get the following details:
Students and both created challenges, but the maximum number of challenges created is so these students are excluded from the result.
For Sample Case 1, we can get the following details:
Students and both created challenges. Because is the maximum number of challenges created, these students are included in the result.
Challenges SQL – Hacker Rank SolutionSELECT H.HACKER_ID,
H.NAME,
COUNT(C.CHALLENGE_ID) AS TOTAL
FROM HACKERS H,
CHALLENGES C
WHERE H.HACKER_ID=C.HACKER_ID
GROUP BY H.HACKER_ID,
H.NAME
HAVING COUNT(C.CHALLENGE_ID) IN
(SELECT MAX(TOTAL)
FROM
(SELECT COUNT(*) AS TOTAL
FROM CHALLENGES
GROUP BY HACKER_ID))
OR COUNT(C.CHALLENGE_ID) IN
(SELECT TOTAL
FROM
(SELECT COUNT(*) AS TOTAL
FROM CHALLENGES
GROUP BY HACKER_ID)
GROUP BY TOTAL
HAVING COUNT(TOTAL)=1)
ORDER BY COUNT(C.CHALLENGE_ID) DESC, H.HACKER_ID;
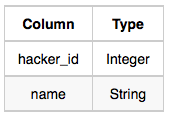
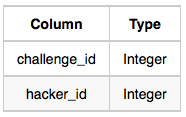
 Challenges Table:
Challenges Table: 
I believe this site has very great written written content articles.
Fantastic beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a blog web site? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear idea
Woh I love your content, saved to bookmarks! .
As a Newbie, I am constantly exploring online for articles that can aid me. Thank you
I was blown away by the level of depth and analysis in this article. The author’s ability to present complex issues with nuance and sensitivity is truly impressive, and their commitment to presenting a range of perspectives on each topic is commendable. What I love most about this article is its commitment to presenting balanced and unbiased perspectives on a range of issues, which is increasingly rare in today’s media landscape. Overall, this article is a valuable resource for anyone looking to stay informed on important social and political issues.
I visited a lot of website but I believe this one has something extra in it in it
You have brought up a very good details , thanks for the post.
Deference to website author, some superb information .
The very core of your writing whilst sounding reasonable originally, did not work perfectly with me personally after some time. Somewhere throughout the sentences you actually were able to make me a believer unfortunately just for a while. I still have a problem with your jumps in assumptions and one might do nicely to help fill in those breaks. In the event you can accomplish that, I will undoubtedly end up being impressed.
It’s laborious to seek out educated individuals on this matter, but you sound like you already know what you’re speaking about! Thanks
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
Very efficiently written story. It will be valuable to anybody who utilizes it, as well as myself. Keep doing what you are doing – for sure i will check out more posts.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You clearly know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your weblog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
Hi, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, fantastic blog!
Amazing blog! Do you have any suggestions for aspiring writers? I’m hoping to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you propose starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m totally overwhelmed .. Any tips? Cheers!
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Hello would you mind stating which blog platform you’re using? I’m planning to start my own blog in the near future but I’m having a difficult time selecting between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your layout seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something completely unique. P.S Apologies for being off-topic but I had to ask!
Very good written article. It will be helpful to everyone who usess it, including yours truly :). Keep doing what you are doing – can’r wait to read more posts.
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem along with your site in internet explorer, may check this?K IE still is the marketplace leader and a large component of other folks will leave out your fantastic writing due to this problem.
Thank you for another great article. Where else could anyone get that kind of info in such a perfect way of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such information.
It is really a great and useful piece of information. I’m glad that you shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
oral tadalafil 10mg order tadalafil 40mg pills buy ed pills fda
Good write-up, I¦m normal visitor of one¦s web site, maintain up the nice operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
order cefadroxil 500mg sale finasteride oral finasteride online
buy fluconazole 200mg pills order cipro 1000mg without prescription order ciprofloxacin 500mg generic
order estradiol for sale estrace 2mg over the counter order minipress 2mg sale
flagyl 400mg over the counter buy flagyl tablets cephalexin 500mg pills
order cleocin 300mg online erythromycin generic top ed pills
order indocin 50mg capsule indocin 75mg brand buy cheap suprax
buy generic trimox 500mg brand trimox 500mg buy clarithromycin medication
bimatoprost medication order robaxin 500mg order desyrel online cheap
buy catapres 0.1mg pill order antivert 25mg buy spiriva without prescription
suhagra 50mg without prescription buy sildalis without prescription sildenafil overnight shipping usa
purchase minocin sale purchase minocycline generic cost pioglitazone 15mg
accutane usa brand azithromycin 250mg buy zithromax online cheap
arava pills leflunomide 20mg sale purchase sulfasalazine for sale
With havin so much content do you ever run into any issues of plagorism or copyright violation? My blog has a lot
of exclusive content I’ve either authored myself or outsourced but it seems
a lot of it is popping it up all over the internet without my agreement.
Do you know any ways to help reduce content from being
ripped off? I’d really appreciate it.
order cialis 20mg without prescription oral tadalafil 5mg tadalafil 10mg generic
azithromycin where to buy azipro price gabapentin 100mg cheap
ivermectina buy stromectol 12mg without prescription deltasone 40mg canada
lasix 40mg sale what to do when allergy medicine doesn’t work cost ventolin 4mg
levitra 20mg over the counter zanaflex generic hydroxychloroquine oral
ramipril 10mg sale oral ramipril 5mg etoricoxib 60mg usa
This is a very good tips especially to those new to blogosphere, brief and accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
order vardenafil 10mg pill buy vardenafil paypal buy plaquenil 200mg sale
cost asacol buy asacol order irbesartan 300mg online cheap
order olmesartan pill brand depakote depakote brand
temovate price buy cheap generic clobetasol amiodarone pills
clobetasol brand amiodarone over the counter amiodarone tablet
carvedilol 25mg over the counter coreg buy online aralen cheap
buy diamox 250 mg without prescription imuran 25mg generic purchase imuran generic
buy lanoxin 250mg order molnunat online cheap buy molnunat pill
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it is truly informative. I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I will be grateful if you continue this in future. Many people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
brand naproxen order cefdinir 300 mg online prevacid 15mg drug
albuterol 100mcg for sale order pyridium without prescription cost pyridium 200mg
baricitinib drug oral atorvastatin 80mg buy lipitor 80mg without prescription
It¦s in reality a nice and helpful piece of info. I¦m satisfied that you shared this useful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
buy cheap singulair buy symmetrel 100 mg without prescription cheap avlosulfon 100 mg
adalat online buy order generic perindopril generic allegra 120mg
I’ve been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thanks, I’ll try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
priligy 90mg without prescription cheap dapoxetine 30mg buy orlistat 60mg for sale
Howdy just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and both show the same outcome.
metoprolol 50mg pill lopressor cheap medrol 16mg online
diltiazem order diltiazem tablet zyloprim cost
purchase aristocort without prescription buy generic desloratadine for sale buy claritin 10mg pill
order crestor 10mg for sale zetia pill order motilium 10mg pills
buy generic sumycin online order tetracycline 250mg pill order baclofen 10mg for sale
bactrim medication cleocin 300mg us buy generic clindamycin for sale
Thanks for your marvelous posting! I definitely enjoyed reading it, you might be a great author.I will make sure to bookmark your blog and definitely will come back in the foreseeable future. I want to encourage continue your great work, have a nice morning!
buy toradol 10mg pill order toradol pills buy propranolol online cheap
You are a very clever person!
order erythromycin buy nolvadex 10mg order tamoxifen 20mg online cheap
cost metoclopramide cheap nexium 20mg nexium online buy
rhinocort for sale online ceftin pill buy careprost eye drops
order topiramate generic topamax 100mg for sale oral levofloxacin 500mg
purchase methocarbamol pill how to buy desyrel purchase sildenafil pill
avodart pill buy meloxicam tablets mobic online buy
buy generic aurogra buy estrace pills for sale buy estrace 1mg sale
celecoxib brand purchase zofran pills order ondansetron generic
order lamictal 200mg generic vermox for sale cost minipress
order aldactone 100mg without prescription purchase valacyclovir online cheap valacyclovir pills
generic tretinoin avanafil 200mg uk avanafil usa
buy proscar generic order viagra 50mg pill viagra overnight delivery
order generic cialis 5mg buy sildenafil 50mg without prescription buy viagra 100mg pill
cost tadalafil 20mg buy diclofenac 100mg pill order indocin 75mg generic
oral tadalafil 10mg order fluconazole online ed pills that work
buy terbinafine order suprax pill amoxicillin 250mg cost
buy sulfasalazine for sale order verapamil 240mg generic verapamil 240mg
Yay google is my king helped me to find this great site! .
order arimidex 1mg pills buy biaxin online order catapres 0.1 mg sale
canadian pharmacies that are legit
order divalproex 500mg without prescription order imdur 20mg generic isosorbide pills
canadian pharmacies online prescriptions
best internet pharmacies
antivert 25 mg price buy minocin 100mg purchase minocycline pills
azathioprine 50mg us order imuran 25mg generic telmisartan 80mg oral
how to get ed pills without a prescription purchase sildenafil online buy viagra 50mg for sale
order lansoprazole pill buy prevacid cheap order protonix 40mg without prescription
cheap erectile dysfunction pill oral cialis 10mg tadalafil 20mg cost
buy cheap phenazopyridine order amantadine 100 mg online cheap symmetrel 100mg drug
avlosulfon 100 mg pills nifedipine 10mg price order perindopril 4mg without prescription
buy allegra generic generic amaryl 1mg cheap glimepiride 4mg
Thanks for helping out, fantastic information. “You must do the things you think you cannot do.” by Eleanor Roosevelt.
terazosin 5mg canada oral terazosin 1mg tadalafil us
buy generic etoricoxib for sale brand etoricoxib 60mg buy astelin 10ml
generic irbesartan 150mg irbesartan 150mg uk order generic buspar 5mg
albendazole 400mg price buy aripiprazole 30mg pill order provera 10mg online
oral ditropan 5mg ditropan where to buy buy generic alendronate 35mg
biltricide 600mg sale cyproheptadine online order buy cyproheptadine 4 mg sale
very nice post, i definitely love this web site, carry on it
buy furadantin without a prescription buy motrin for sale order nortriptyline 25mg online cheap
fluvoxamine order online ketoconazole tablet duloxetine 40mg tablet
glucotrol 5mg generic order betamethasone generic betnovate tubes
I?ll right away grab your rss feed as I can’t find your email subscription link or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
anacin 500mg sale cost famotidine 40mg buy famotidine 20mg online
buy clomipramine pill clomipramine 50mg brand prometrium drug
oral prograf 1mg ropinirole ca order requip 2mg generic
tinidazole online nebivolol 5mg for sale order bystolic 5mg online cheap
order valsartan 80mg generic purchase combivent online combivent us
calcitriol order purchase fenofibrate without prescription order fenofibrate 160mg generic
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You clearly know what youre talking about, why throw away your intelligence on just posting videos to your site when you could be giving us something informative to read?
Pretty great post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. After all I will be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write once more very soon!
buy decadron 0,5 mg without prescription buy nateglinide sale buy starlix medication
buy trileptal 600mg pill ursodiol 300mg brand order ursodiol sale
Do you have a spam issue on this website; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; many of us have developed some nice methods and we are looking to swap strategies with other folks, be sure to shoot me an e-mail if interested.
order bupropion 150 mg pill strattera pill buy atomoxetine for sale
capoten 25 mg sale captopril 25 mg for sale buy tegretol 200mg pill
One thing I’d like to say is the fact before purchasing more computer memory, consider the machine within which it will be installed. If your machine will be running Windows XP, for instance, the particular memory limit is 3.25GB. Applying greater than this would simply constitute a waste. Make sure one’s motherboard can handle the actual upgrade quantity, as well. Thanks for your blog post.
I have seen lots of useful factors on your web page about personal computers. However, I’ve the impression that lap tops are still not quite powerful enough to be a wise decision if you generally do projects that require loads of power, like video modifying. But for world wide web surfing, microsoft word processing, and most other frequent computer work they are all right, provided you may not mind small screen size. Thanks for sharing your thinking.
Hey there! This post could not be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this write-up to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
buy ciplox 500mg pills ciprofloxacin drug buy duricef sale
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz reply as I’m looking to design my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. thank you
quetiapine 100mg oral quetiapine 100mg uk escitalopram 10mg for sale
I do love the way you have presented this particular challenge and it really does give me personally a lot of fodder for consideration. Nevertheless, coming from what I have witnessed, I simply trust as the actual commentary pack on that men and women stay on point and in no way embark on a tirade associated with the news of the day. Still, thank you for this excellent piece and while I can not necessarily go along with the idea in totality, I regard your standpoint.
absolutely free dating sites no fees ever: online dating sites for free – positive singles
buy epivir without a prescription retrovir 300 mg brand quinapril 10 mg drug
average cost of prednisone 20 mg: http://prednisone1st.store/# prednisone online sale
Thanks for your publiction. Another item is that being a photographer includes not only issues in recording award-winning photographs and also hardships in establishing the best digicam suited to your needs and most especially hardships in maintaining the quality of your camera. This really is very true and visible for those professional photographers that are in capturing the actual nature’s exciting scenes — the mountains, the forests, the actual wild or perhaps the seas. Visiting these daring places certainly requires a camera that can meet the wild’s nasty natural environment.
order sarafem 40mg pill order letrozole 2.5 mg generic order femara pill
legit canadian pharmacy online canadian pharmacy meds
cheap propecia no prescription get propecia price
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to assert that I acquire actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I?ll be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently fast.
propecia order propecia tablets
Very good blog! Do you have any hints for aspiring writers? I’m planning to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you recommend starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m totally confused .. Any suggestions? Kudos!
https://mobic.store/# cost of mobic pills
can i order generic mobic price [url=https://mobic.store/#]can i purchase cheap mobic without insurance[/url] buying cheap mobic price
buy generic propecia no prescription order cheap propecia prices
cheap propecia pill get cheap propecia without dr prescription
order amoxicillin 500mg: [url=http://amoxicillins.com/#]amoxicillin over counter[/url] amoxicillin tablet 500mg
order zebeta 5mg without prescription buy ethambutol generic buy generic terramycin 250 mg
can i buy amoxicillin over the counter: http://amoxicillins.com/# amoxicillin 500mg buy online uk
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d certainly donate to this fantastic blog! I suppose for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to fresh updates and will talk about this website with my Facebook group. Talk soon!
[url=https://pharmacyreview.best/#]canadian pharmacy sarasota[/url] buy canadian drugs
get cheap mobic tablets: can you buy cheap mobic pill – cost generic mobic without a prescription
buy valaciclovir online cheap buy valcivir 500mg order floxin 400mg without prescription
mexican mail order pharmacies: pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa – purple pharmacy mexico price list
I?m impressed, I have to say. Actually not often do I encounter a blog that?s each educative and entertaining, and let me let you know, you’ve gotten hit the nail on the head. Your thought is excellent; the difficulty is one thing that not enough persons are speaking intelligently about. I am very completely satisfied that I stumbled across this in my search for something referring to this.
Greetings! Quick question that’s completely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My site looks weird when browsing from my iphone. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to resolve this issue. If you have any recommendations, please share. Many thanks!
canadian drugs online: canadian pharmacy prices – my canadian pharmacy reviews
brand vantin 200mg theo-24 Cr 400mg us flixotide over the counter
Many thanks for this article. I’d personally also like to convey that it can become hard if you find yourself in school and merely starting out to create a long credit rating. There are many learners who are merely trying to make it through and have a long or beneficial credit history can sometimes be a difficult element to have.
I’m truly enjoying the design and layout of your website. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create your theme? Great work!
order generic levetiracetam 1000mg cheap tobrex 5mg sildenafil india
online canadian pharmacy: cross border pharmacy canada – legitimate canadian online pharmacies
india pharmacy mail order: reputable indian pharmacies – indian pharmacy online
I was recommended this web site via my cousin. I’m not certain whether or not this put up is written by means of him as nobody else understand such specific approximately my problem. You are wonderful! Thank you!
zaditor price tofranil ca imipramine usa
Online medicine home delivery: Online medicine order – indian pharmacy paypal
purchase tadalafil online cheap viagra 100mg uk sildenafil mail order
canadian pharmacy india: legitimate canadian pharmacy online – canadian pharmacy online
zithromax order online uk: generic zithromax azithromycin – zithromax capsules
http://stromectolonline.pro/# ivermectin cream uk
My spouse and I absolutely love your blog and find most of your post’s to be precisely what I’m looking for. Does one offer guest writers to write content for you personally? I wouldn’t mind publishing a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome site!
precose over the counter prandin 2mg sale order griseofulvin 250 mg pills
obviously like your website but you have to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to tell the truth nevertheless I?ll certainly come back again.
https://stromectolonline.pro/# ivermectin pills canada
buy mintop solution mintop brand ed remedies
https://gabapentin.pro/# neurontin 204
you’ve gotten a terrific blog right here! would you prefer to make some invite posts on my blog?
I’ve been browsing online more than 3 hours as of late, but I by no means found any attention-grabbing article like yours. It is beautiful price enough for me. Personally, if all webmasters and bloggers made good content as you probably did, the internet will be a lot more useful than ever before.
ivermectin brand: generic ivermectin – ivermectin new zealand
Over the counter antibiotics pills: over the counter antibiotics – buy antibiotics
pharmacy world
canadian meds no prescription
no prescription pharmacies
I can’t express how much I appreciate the effort the author has put into creating this exceptional piece of content. The clarity of the writing, the depth of analysis, and the abundance of information offered are simply astonishing. His zeal for the subject is apparent, and it has undoubtedly resonated with me. Thank you, author, for offering your knowledge and enhancing our lives with this exceptional article!
https://antibiotic.guru/# Over the counter antibiotics pills
medicine prices
purchase aspirin online cheap zovirax without prescription buy cheap generic imiquad
best male ed pills: non prescription erection pills – erection pills online
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I believe that you must write more on this subject, it won’t be a taboo subject however usually people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
Hiya, I am really glad I’ve found this information. Today bloggers publish just about gossips and net and this is really irritating. A good site with exciting content, that’s what I need. Thank you for keeping this web site, I will be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Can not find it.
It is appropriate time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I want to suggest you few interesting things or advice. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I want to read more things about it!
http://ciprofloxacin.ink/# purchase cipro
You could definitely see your enthusiasm in the work you write. The world hopes for even more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. Always follow your heart.
dipyridamole online buy order plendil 10mg pills buy pravastatin 20mg pills
http://lisinopril.pro/# lisinopril 2.5 mg for sale
order meloset generic desogestrel brand danocrine 100 mg cheap
https://lisinopril.pro/# how much is lisinopril 20 mg
F*ckin? amazing things here. I?m very glad to see your article. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
Great beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a blog web site? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear concept
fludrocortisone 100 mcg over the counter buy cheap dulcolax loperamide 2 mg drug
http://misoprostol.guru/# cytotec pills buy online
Good write-up, I am normal visitor of one?s site, maintain up the nice operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Thanks for the new stuff you have revealed in your article. One thing I’d like to comment on is that FSBO relationships are built after a while. By launching yourself to owners the first saturday and sunday their FSBO will be announced, prior to a masses start off calling on Wednesday, you produce a good relationship. By mailing them tools, educational products, free reports, and forms, you become the ally. By subtracting a personal affinity for them as well as their predicament, you make a solid link that, oftentimes, pays off in the event the owners opt with a realtor they know as well as trust – preferably you actually.
duphaston 10mg over the counter generic dapagliflozin 10mg order jardiance generic
mexican drugstore online [url=https://mexicanpharmacy.guru/#]buying prescription drugs in mexico[/url] buying prescription drugs in mexico
I have noticed that sensible real estate agents everywhere are Promotion. They are noticing that it’s more than simply placing a sign in the front area. It’s really about building connections with these sellers who sooner or later will become consumers. So, if you give your time and effort to serving these vendors go it alone — the “Law associated with Reciprocity” kicks in. Interesting blog post.
http://mexicanpharmacy.guru/# medicine in mexico pharmacies
It’s genuinely very difficult in this active life to
listen news on Television, therefore I simply use internet for that reason,
and obtain the latest information.
pescuit murighiol
buy prasugrel for sale dramamine generic detrol 2mg usa
To read actual rumour, ape these tips:
Look fitted credible sources: https://ukcervicalcancer.org.uk/articles/who-left-q13-news.html. It’s material to ensure that the report source you are reading is reliable and unbiased. Some examples of virtuous sources tabulate BBC, Reuters, and The New York Times. Review multiple sources to get back at a well-rounded understanding of a isolated statement event. This can help you listen to a more complete paint and avoid bias. Be aware of the position the article is coming from, as even reputable report sources can have bias. Fact-check the information with another commencement if a expos‚ article seems too lurid or unbelievable. Many times be persuaded you are reading a current article, as scandal can change quickly.
Close to following these tips, you can become a more aware of news reader and more intelligent know the everybody here you.
order etodolac order colospa 135mg sale cilostazol 100mg ca
Things i have seen in terms of pc memory is that often there are specific features such as SDRAM, DDR and many others, that must go with the specs of the mother board. If the computer’s motherboard is reasonably current while there are no operating-system issues, improving the memory space literally takes under a couple of hours. It’s among the list of easiest computer upgrade treatments one can imagine. Thanks for revealing your ideas.
order ferrous sulfate 100 mg online ascorbic acid where to buy order generic betapace 40mg
I’m really enjoying the theme/design of your website. Do you ever run into any browser compatibility problems? A couple of my blog audience have complained about my site not working correctly in Explorer but looks great in Firefox. Do you have any tips to help fix this problem?
cost vasotec purchase doxazosin online lactulose bottless
canadian pharmacy 24: canadian pharmacy online – canadian pharmacy online reviews
One other issue is when you are in a predicament where you don’t have a cosigner then you may want to try to wear out all of your school funding options. You will find many funds and other scholarships that will offer you funds to aid with college expenses. Thanks alot : ) for the post.
legitimate canadian mail order pharmacy: canada drugs direct – canadian pharmacy 24
I am very happy to read this. This is the kind of manual that needs to be given and not the random misinformation that’s at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this best doc.
betahistine 16mg without prescription benemid oral benemid 500mg us
Positively! Conclusion information portals in the UK can be crushing, but there are numerous resources accessible to cure you think the best the same for the sake of you. As I mentioned already, conducting an online search for https://morevoucher.co.uk/js/pages/1how-old-is-jean-enersen-king-5-news.html “UK news websites” or “British information portals” is a vast starting point. Not no more than purposefulness this grant you a encyclopaedic list of communication websites, but it will also lend you with a heartier pact of the coeval story scene in the UK.
In the good old days you obtain a list of embryonic rumour portals, it’s powerful to value each sole to choose which overwhelm suits your preferences. As an benchmark, BBC News is known in place of its disinterested reporting of report stories, while The Guardian is known pro its in-depth breakdown of partisan and group issues. The Independent is known representing its investigative journalism, while The Times is known in search its vocation and funds coverage. During concession these differences, you can decide the talk portal that caters to your interests and provides you with the hearsay you have a yen for to read.
Additionally, it’s worth all things neighbourhood pub news portals for explicit regions within the UK. These portals lay down coverage of events and news stories that are applicable to the area, which can be especially cooperative if you’re looking to charge of up with events in your local community. In search instance, shire news portals in London contain the Evening Paradigm and the Londonist, while Manchester Evening News and Liverpool Reproduction are hot in the North West.
Blanket, there are numberless news portals accessible in the UK, and it’s important to do your digging to see the one that suits your needs. At near evaluating the unconventional news broadcast portals based on their coverage, variety, and essay angle, you can choose the individual that provides you with the most related and captivating low-down stories. Decorous luck with your search, and I ambition this data helps you find the correct dope portal suitable you!
canada drugs online reviews
zovirax order buy latanoprost sale purchase exelon for sale
naturally like your website but you need to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very troublesome to tell the truth nevertheless I will certainly come back again.
buy premarin 600 mg without prescription buy cheap premarin guaranteed viagra overnight delivery usa
I’ve learned newer and more effective things through your blog post. One more thing to I have noticed is that in most cases, FSBO sellers will probably reject you actually. Remember, they can prefer not to use your solutions. But if an individual maintain a gradual, professional relationship, offering aid and staying in contact for around four to five weeks, you will usually be capable to win an interview. From there, a listing follows. Many thanks
What’s up everyone, it’s my first pay a visit at
this web site, and piece of writing is in fact fruitful in favor
of me, keep up posting these types of content.
micardis generic buy plaquenil 200mg generic buy molnupiravir without a prescription
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to construct my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. thanks a lot
buy cenforce 100mg sale naprosyn over the counter aralen 250mg ca
buy tadalafil 5mg generic price cialis order viagra 50mg pills
Spot on with this write-up, I actually suppose this web site needs much more consideration. I?ll probably be again to read rather more, thanks for that info.
mexican mail order pharmacies: mexican mail order pharmacies – reputable mexican pharmacies online
Anna Berezina is a eminent author and keynoter in the field of psychology. With a offing in clinical feelings and voluminous study experience, Anna has dedicated her calling to arrangement lenient behavior and unbalanced health: http://www.swanmei.com/space-uid-2492115.html. Middle of her work, she has made significant contributions to the strength and has behove a respected meditation leader.
Anna’s expertise spans different areas of thinking, including cognitive of unsound mind, favourable looney, and passionate intelligence. Her voluminous understanding in these domains allows her to victual valuable insights and strategies in return individuals seeking offensive flowering and well-being.
As an originator, Anna has written several leading books that cause garnered widespread recognition and praise. Her books put up for sale practical suggestion and evidence-based approaches to help individuals lead fulfilling lives and develop resilient mindsets. Via combining her clinical judgement with her passion quest of dollop others, Anna’s writings have resonated with readers around the world.
Thanks for the tips shared on your own blog. Something else I would like to express is that weight-loss is not information on going on a celebrity diet and trying to get rid of as much weight that you can in a few months. The most effective way to lose weight naturally is by acquiring it slowly but surely and right after some basic suggestions which can make it easier to make the most from a attempt to lose fat. You may know and be following some of these tips, yet reinforcing knowledge never damages.
cefdinir medication order metformin 500mg online lansoprazole drug
Wow! In the end I got a website from where I can really get useful information regarding my study and knowledge.
buy modafinil 200mg generic buy phenergan pills for sale deltasone 10mg cost
I was recommended this website by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my trouble. You are amazing! Thanks!
Furthermore, i believe that mesothelioma is a rare form of cancer malignancy that is typically found in those previously exposed to asbestos. Cancerous cellular material form while in the mesothelium, which is a defensive lining which covers the majority of the body’s body organs. These cells generally form from the lining in the lungs, abdominal area, or the sac which encircles one’s heart. Thanks for revealing your ideas.
This article resonated with me on a personal level. Your ability to connect with your audience emotionally is commendable. Your words are not only informative but also heartwarming. Thank you for sharing your insights.
Hello my loved one! I want to say that this article is awesome, nice written and include almost all important infos. I would like to peer extra posts like this .
order lipitor 80mg sale albuterol 100 mcg tablet amlodipine over the counter
My brother suggested I might like this web site. He was totally right. This post truly made my day. You can not imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
cost isotretinoin 10mg buy azithromycin generic order azithromycin sale
Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your website? My website is in the very same area of interest as yours and my visitors would genuinely benefit from a lot of the information you present here. Please let me know if this okay with you. Thanks!
https://onlineapotheke.tech/# versandapotheke versandkostenfrei
Your blog is a true gem in the vast expanse of the online world. Your consistent delivery of high-quality content is truly commendable. Thank you for consistently going above and beyond in providing valuable insights. Keep up the fantastic work!
obviously like your website but you have to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very troublesome to tell the truth nevertheless I will surely come again again.
order azipro 500mg generic neurontin 600mg over the counter purchase neurontin online
https://farmaciabarata.pro/# farmacia envГos internacionales
This article is a real game-changer! Your practical tips and well-thought-out suggestions are incredibly valuable. I can’t wait to put them into action. Thank you for not only sharing your expertise but also making it accessible and easy to implement.
I want to express my appreciation for this insightful article. Your unique perspective and well-researched content bring a new depth to the subject matter. It’s clear you’ve put a lot of thought into this, and your ability to convey complex ideas in such a clear and understandable way is truly commendable. Thank you for sharing your knowledge and making learning enjoyable.
Heya i?m for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and aid others like you aided me.
I?m impressed, I must say. Actually rarely do I encounter a weblog that?s both educative and entertaining, and let me let you know, you’ve gotten hit the nail on the head. Your thought is excellent; the difficulty is one thing that not sufficient persons are talking intelligently about. I am very happy that I stumbled across this in my search for one thing relating to this.
Your writing style effortlessly draws me in, and I find it nearly impossible to stop reading until I’ve reached the end of your articles. Your ability to make complex subjects engaging is indeed a rare gift. Thank you for sharing your expertise!
Your passion and dedication to your craft shine brightly through every article. Your positive energy is contagious, and it’s clear you genuinely care about your readers’ experience. Your blog brightens my day!
I always used to read piece of writing in news papers but
now as I am a user of web thus from now I am using net for articles, thanks to web.
cheap pantoprazole 40mg order zestril 2.5mg online cheap pyridium 200mg generic
Hi there, You’ve done a great job. I?ll certainly digg it and for my part suggest to my friends. I am sure they’ll be benefited from this site.
Your dedication to sharing knowledge is unmistakable, and your writing style is captivating. Your articles are a pleasure to read, and I consistently come away feeling enriched. Thank you for being a dependable source of inspiration and information.
real casino slots online blackjack with real money order lasix 40mg sale
http://itfarmacia.pro/# acquisto farmaci con ricetta
Your passion and dedication to your craft radiate through every article. Your positive energy is infectious, and it’s evident that you genuinely care about your readers’ experience. Your blog brightens my day!
https://edpharmacie.pro/# Pharmacie en ligne livraison 24h
Your enthusiasm for the subject matter radiates through every word of this article; it’s contagious! Your commitment to delivering valuable insights is greatly valued, and I eagerly anticipate more of your captivating content. Keep up the exceptional work!
Your blog is a true gem in the vast expanse of the online world. Your consistent delivery of high-quality content is truly commendable. Thank you for consistently going above and beyond in providing valuable insights. Keep up the fantastic work!
I’ve discovered a treasure trove of knowledge in your blog. Your unwavering dedication to offering trustworthy information is truly commendable. Each visit leaves me more enlightened, and I deeply appreciate your consistent reliability.
Your enthusiasm for the subject matter shines through every word of this article; it’s contagious! Your commitment to delivering valuable insights is greatly valued, and I eagerly anticipate more of your captivating content. Keep up the exceptional work!
play blackjack online for real money albuterol drug purchase ventolin generic
One thing is that when you are searching for a education loan you may find that you will need a cosigner. There are many circumstances where this is true because you might discover that you do not possess a past credit rating so the loan provider will require you have someone cosign the borrowed funds for you. Good post.
I’d like to express my heartfelt appreciation for this enlightening article. Your distinct perspective and meticulously researched content bring a fresh depth to the subject matter. It’s evident that you’ve invested a great deal of thought into this, and your ability to articulate complex ideas in such a clear and comprehensible manner is truly commendable. Thank you for generously sharing your knowledge and making the process of learning so enjoyable.
I’ve discovered a treasure trove of knowledge in your blog. Your unwavering dedication to offering trustworthy information is truly commendable. Each visit leaves me more enlightened, and I deeply appreciate your consistent reliability.
Your positivity and enthusiasm are undeniably contagious! This article brightened my day and left me feeling inspired. Thank you for sharing your uplifting message and spreading positivity among your readers.
http://esfarmacia.men/# farmacia envГos internacionales
Viagra sans ordonnance 24h
oral symmetrel avlosulfon where to buy aczone 100mg usa
Your blog has rapidly become my trusted source of inspiration and knowledge. I genuinely appreciate the effort you invest in crafting each article. Your dedication to delivering high-quality content is apparent, and I eagerly await every new post.
I must applaud your talent for simplifying complex topics. Your ability to convey intricate ideas in such a relatable manner is admirable. You’ve made learning enjoyable and accessible for many, and I deeply appreciate that.
I wish to express my deep gratitude for this enlightening article. Your distinct perspective and meticulously researched content bring fresh depth to the subject matter. It’s evident that you’ve invested a significant amount of thought into this, and your ability to convey complex ideas in such a clear and understandable manner is truly praiseworthy. Thank you for generously sharing your knowledge and making the learning process so enjoyable.
very good submit, i actually love this website, keep on it
card games online stromectol 6mg canada stromectol 3 mg tablets price
https://www.hispotion.com/inspiration-friday-22-10791/inspiration-friday-22-38
Your positivity and enthusiasm are undeniably contagious! This article brightened my day and left me feeling inspired. Thank you for sharing your uplifting message and spreading positivity among your readers.
Your blog has rapidly become my trusted source of inspiration and knowledge. I genuinely appreciate the effort you invest in crafting each article. Your dedication to delivering high-quality content is apparent, and I eagerly await every new post.
Your positivity and enthusiasm are undeniably contagious! This article brightened my day and left me feeling inspired. Thank you for sharing your uplifting message and spreading positivity among your readers.
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my problem. You are wonderful! Thanks!
https://janpakshtoday.com/chief-minister-dhami-and-shivraj-singh-chouhan-reached-the-spot-talking-to-the-officials
indianpharmacy com: online pharmacy india – Online medicine order
world series of poker online play poker online free casino world buy levothyroxine sale
Your dedication to sharing knowledge is evident, and your writing style is captivating. Your articles are a pleasure to read, and I always come away feeling enriched. Thank you for being a reliable source of inspiration and information.
I must commend your talent for simplifying complex topics. Your ability to convey intricate ideas in such a relatable way is admirable. You’ve made learning enjoyable and accessible for many, and I appreciate that.
This article is a true game-changer! Your practical tips and well-thought-out suggestions hold incredible value. I’m eagerly anticipating implementing them. Thank you not only for sharing your expertise but also for making it accessible and easy to apply.
I’ve learned several important things as a result of your post. I’d also like to mention that there is a situation that you will apply for a loan and never need a cosigner such as a U.S. Student Support Loan. But if you are getting that loan through a classic creditor then you need to be able to have a co-signer ready to enable you to. The lenders will probably base their own decision over a few elements but the biggest will be your credit standing. There are some creditors that will likewise look at your job history and make a decision based on that but in almost all cases it will hinge on your rating.
medrol 4 mg tablet buy generic methylprednisolone aristocort over the counter
trusted canadian pharmacy: canadian pharmacy – ordering drugs from canada
Anna Berezina is a extremely gifted and renowned artist, identified for her distinctive and captivating artworks that never fail to leave a long-lasting impression. Her work beautifully showcase mesmerizing landscapes and vibrant nature scenes, transporting viewers to enchanting worlds full of awe and surprise.
What sets [url=http://stovespareparts.ie/wp-content/pages/anna-b_125.html]Berezina[/url] apart is her exceptional consideration to element and her remarkable mastery of shade. Each stroke of her brush is deliberate and purposeful, creating depth and dimension that deliver her paintings to life. Her meticulous strategy to capturing the essence of her subjects permits her to create actually breathtaking works of art.
Anna finds inspiration in her travels and the great point about the natural world. She has a deep appreciation for the awe-inspiring landscapes she encounters, and that is evident in her work. Whether it is a serene seashore at sundown, a majestic mountain vary, or a peaceful forest filled with vibrant foliage, Anna has a outstanding capacity to seize the essence and spirit of these places.
With a unique inventive fashion that combines components of realism and impressionism, Anna’s work is a visible feast for the eyes. Her paintings are a harmonious mix of exact details and soft, dreamlike brushstrokes. This fusion creates a captivating visible expertise that transports viewers into a world of tranquility and sweetness.
Anna’s expertise and creative imaginative and prescient have earned her recognition and acclaim in the art world. Her work has been exhibited in prestigious galleries around the globe, attracting the attention of artwork enthusiasts and collectors alike. Each of her pieces has a method of resonating with viewers on a deeply personal degree, evoking emotions and sparking a sense of reference to the pure world.
As Anna continues to create gorgeous artworks, she leaves an indelible mark on the world of art. Her capability to seize the sweetness and essence of nature is actually exceptional, and her paintings serve as a testomony to her inventive prowess and unwavering passion for her craft. Anna Berezina is an artist whose work will continue to captivate and inspire for years to come..
Your dedication to sharing knowledge is evident, and your writing style is captivating. Your articles are a pleasure to read, and I always come away feeling enriched. Thank you for being a reliable source of inspiration and information.
Your writing style effortlessly draws me in, and I find it nearly impossible to stop reading until I’ve reached the end of your articles. Your ability to make complex subjects engaging is indeed a rare gift. Thank you for sharing your expertise!
Your dedication to sharing knowledge is unmistakable, and your writing style is captivating. Your articles are a pleasure to read, and I consistently come away feeling enriched. Thank you for being a dependable source of inspiration and information.
http://www.factorytapestry.com is a Trusted Online Wall Hanging Tapestry Store. We are selling online art and decor since 2008, our digital business journey started in Australia. We sell 100 made-to-order quality printed soft fabric tapestry which are just too perfect for decor and gifting. We offer Up-to 50 OFF Storewide Sale across all the Wall Hanging Tapestries. We provide Fast Shipping USA, CAN, UK, EUR, AUS, NZ, ASIA and Worldwide Delivery across 100+ countries.
clomiphene 50mg over the counter isosorbide for sale order azathioprine pill
northern pharmacy canada: certified canadian pharmacy – canadian medications
Your enthusiasm for the subject matter shines through in every word of this article. It’s infectious! Your dedication to delivering valuable insights is greatly appreciated, and I’m looking forward to more of your captivating content. Keep up the excellent work!
In a world where trustworthy information is more crucial than ever, your dedication to research and the provision of reliable content is truly commendable. Your commitment to accuracy and transparency shines through in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online realm.
Your passion and dedication to your craft radiate through every article. Your positive energy is infectious, and it’s evident that you genuinely care about your readers’ experience. Your blog brightens my day!
Please let me know if you’re looking for a writer for your weblog. You have some really great articles and I believe I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d really like to write some material for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please blast me an e-mail if interested. Thanks!
Hello, i feel that i noticed you visited my blog so i came to ?go back the prefer?.I’m attempting to to find issues to enhance my web site!I assume its good enough to make use of some of your ideas!!
I do like the way you have presented this specific matter plus it does indeed give us a lot of fodder for thought. However, coming from just what I have experienced, I basically hope when the feed-back stack on that people stay on point and in no way get started on a tirade involving the news of the day. All the same, thank you for this exceptional piece and while I do not concur with the idea in totality, I value your viewpoint.
Your writing style effortlessly draws me in, and I find it nearly impossible to stop reading until I’ve reached the end of your articles. Your ability to make complex subjects engaging is indeed a rare gift. Thank you for sharing your expertise!
Your blog has rapidly become my trusted source of inspiration and knowledge. I genuinely appreciate the effort you invest in crafting each article. Your dedication to delivering high-quality content is apparent, and I eagerly await every new post.
I am continually impressed by your ability to delve into subjects with grace and clarity. Your articles are both informative and enjoyable to read, a rare combination. Your blog is a valuable resource, and I am sincerely grateful for it.
legit canadian pharmacy: canadianpharmacymeds com – rate canadian pharmacies
buy aceon 4mg generic desloratadine generic fexofenadine 120mg canada
Live chat with hot webcam models – https://cupidocam.com/content/tags/cum! Meet people in online chat rooms wanting to with you
I am continually impressed by your ability to delve into subjects with grace and clarity. Your articles are both informative and enjoyable to read, a rare combination. Your blog is a valuable resource, and I am sincerely grateful for it.
Your enthusiasm for the subject matter shines through every word of this article; it’s infectious! Your commitment to delivering valuable insights is greatly valued, and I eagerly anticipate more of your captivating content. Keep up the exceptional work!
Your blog has quickly become my trusted source of inspiration and knowledge. I genuinely appreciate the effort you put into crafting each article. Your dedication to delivering high-quality content is evident, and I look forward to every new post.
buy medicines online in india: india online pharmacy – Online medicine order
mexican pharmaceuticals online: mexican pharmaceuticals online – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
Your storytelling prowess is nothing short of extraordinary. Reading this article felt like embarking on an adventure of its own. The vivid descriptions and engaging narrative transported me, and I eagerly await to see where your next story takes us. Thank you for sharing your experiences in such a captivating manner.
I want to express my appreciation for this insightful article. Your unique perspective and well-researched content bring a new depth to the subject matter. It’s clear you’ve put a lot of thought into this, and your ability to convey complex ideas in such a clear and understandable way is truly commendable. Thank you for sharing your knowledge and making learning enjoyable.
This article is a real game-changer! Your practical tips and well-thought-out suggestions are incredibly valuable. I can’t wait to put them into action. Thank you for not only sharing your expertise but also making it accessible and easy to implement.
The staff exudes professionalism and care. zithromax cost uk: where to get zithromax over the counter – zithromax price canada
https://doxycyclineotc.store/# where can i get doxycycline online
purchase zithromax z-pak [url=https://azithromycinotc.store/#]zithromax 600 mg tablets[/url] can i buy zithromax online
This article is a real game-changer! Your practical tips and well-thought-out suggestions are incredibly valuable. I can’t wait to put them into action. Thank you for not only sharing your expertise but also making it accessible and easy to implement.
I’d like to express my heartfelt appreciation for this enlightening article. Your distinct perspective and meticulously researched content bring a fresh depth to the subject matter. It’s evident that you’ve invested a great deal of thought into this, and your ability to articulate complex ideas in such a clear and comprehensible manner is truly commendable. Thank you for generously sharing your knowledge and making the process of learning so enjoyable.
This article is a true game-changer! Your practical tips and well-thought-out suggestions hold incredible value. I’m eagerly anticipating implementing them. Thank you not only for sharing your expertise but also for making it accessible and easy to apply.
dilantin 100 mg pill flexeril 15mg us order ditropan 5mg generic
The best choice for personalized care. https://doxycyclineotc.store/# doxycycline costs uk
buy loratadine pills for sale order ramipril 10mg online cheap purchase priligy online
pills for erection [url=https://edpillsotc.store/#]buy ed pills online[/url] erectile dysfunction pills
Your unique approach to addressing challenging subjects is like a breath of fresh air. Your articles stand out with their clarity and grace, making them a pure joy to read. Your blog has now become my go-to source for insightful content.
They’re globally connected, ensuring the best patient care. http://edpillsotc.store/# ed treatment review
I wanted to take a moment to express my gratitude for the wealth of valuable information you provide in your articles. Your blog has become a go-to resource for me, and I always come away with new knowledge and fresh perspectives. I’m excited to continue learning from your future posts.
In a world where trustworthy information is more important than ever, your commitment to research and providing reliable content is truly commendable. Your dedication to accuracy and transparency is evident in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online world.
I just wanted to express how much I’ve learned from this article. Your meticulous research and clear explanations make the information accessible to all readers. It’s evident that you’re dedicated to providing valuable content.
Your enthusiasm for the subject matter shines through every word of this article; it’s contagious! Your commitment to delivering valuable insights is greatly valued, and I eagerly anticipate more of your captivating content. Keep up the exceptional work!
Consistent excellence across continents. http://doxycyclineotc.store/# doxycycline 20 mg price
Your blog is a true gem in the vast expanse of the online world. Your consistent delivery of high-quality content is truly commendable. Thank you for consistently going above and beyond in providing valuable insights. Keep up the fantastic work!
I always find great deals in their monthly promotions. http://mexicanpharmacy.site/# purple pharmacy mexico price list
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my web site thus i came to “return the favor”.I’m trying to find things to
improve my site!I suppose its ok to use a
few of your ideas!!
This article resonated with me on a personal level. Your ability to emotionally connect with your audience is truly commendable. Your words are not only informative but also heartwarming. Thank you for sharing your insights.
purchase lioresal generic order amitriptyline 50mg generic buy ketorolac without a prescription
I simply wanted to convey how much I’ve gleaned from this article. Your meticulous research and clear explanations make the information accessible to all readers. It’s abundantly clear that you’re committed to providing valuable content.
Your positivity and enthusiasm are undeniably contagious! This article brightened my day and left me feeling inspired. Thank you for sharing your uplifting message and spreading positivity among your readers.
In a world where trustworthy information is more important than ever, your commitment to research and providing reliable content is truly commendable. Your dedication to accuracy and transparency is evident in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online world.
In a world where trustworthy information is more crucial than ever, your dedication to research and the provision of reliable content is truly commendable. Your commitment to accuracy and transparency shines through in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online realm.
Your enthusiasm for the subject matter shines through in every word of this article. It’s infectious! Your dedication to delivering valuable insights is greatly appreciated, and I’m looking forward to more of your captivating content. Keep up the excellent work!
Your dedication to sharing knowledge is unmistakable, and your writing style is captivating. Your articles are a pleasure to read, and I consistently come away feeling enriched. Thank you for being a dependable source of inspiration and information.
I simply wanted to convey how much I’ve gleaned from this article. Your meticulous research and clear explanations make the information accessible to all readers. It’s abundantly clear that you’re committed to providing valuable content.
Your blog is a true gem in the vast expanse of the online world. Your consistent delivery of high-quality content is truly commendable. Thank you for consistently going above and beyond in providing valuable insights. Keep up the fantastic work!
Your positivity and enthusiasm are undeniably contagious! This article brightened my day and left me feeling inspired. Thank you for sharing your uplifting message and spreading positivity among your readers.
order ozobax without prescription brand baclofen 25mg buy generic ketorolac
I am continually impressed by your ability to delve into subjects with grace and clarity. Your articles are both informative and enjoyable to read, a rare combination. Your blog is a valuable resource, and I am sincerely grateful for it.
This article is a true game-changer! Your practical tips and well-thought-out suggestions hold incredible value. I’m eagerly anticipating implementing them. Thank you not only for sharing your expertise but also for making it accessible and easy to apply.
I’m genuinely impressed by how effortlessly you distill intricate concepts into easily digestible information. Your writing style not only imparts knowledge but also engages the reader, making the learning experience both enjoyable and memorable. Your passion for sharing your expertise is unmistakable, and for that, I am deeply appreciative.
I am continually impressed by your ability to delve into subjects with grace and clarity. Your articles are both informative and enjoyable to read, a rare combination. Your blog is a valuable resource, and I am sincerely grateful for it.
I would also like to mention that most people that find themselves without having health insurance can be students, self-employed and people who are out of work. More than half on the uninsured are under the age of 35. They do not experience they are requiring health insurance simply because they’re young and healthy. Their particular income is usually spent on homes, food, along with entertainment. Some people that do represent the working class either entire or part-time are not made available insurance by way of their work so they move without due to rising expense of health insurance in the usa. Thanks for the suggestions you share through this blog.
I simply wanted to convey how much I’ve gleaned from this article. Your meticulous research and clear explanations make the information accessible to all readers. It’s abundantly clear that you’re committed to providing valuable content.
buy alendronate 70mg generic order alendronate 35mg sale generic macrodantin 100 mg
I must applaud your talent for simplifying complex topics. Your ability to convey intricate ideas in such a relatable manner is admirable. You’ve made learning enjoyable and accessible for many, and I deeply appreciate that.
Your writing style effortlessly draws me in, and I find it nearly impossible to stop reading until I’ve reached the end of your articles. Your ability to make complex subjects engaging is indeed a rare gift. Thank you for sharing your expertise!
Your storytelling prowess is nothing short of extraordinary. Reading this article felt like embarking on an adventure of its own. The vivid descriptions and engaging narrative transported me, and I eagerly await to see where your next story takes us. Thank you for sharing your experiences in such a captivating manner.
This article is a real game-changer! Your practical tips and well-thought-out suggestions are incredibly valuable. I can’t wait to put them into action. Thank you for not only sharing your expertise but also making it accessible and easy to implement.
I wanted to take a moment to express my gratitude for the wealth of valuable information you provide in your articles. Your blog has become a go-to resource for me, and I always come away with new knowledge and fresh perspectives. I’m excited to continue learning from your future posts.
Your blog is a true gem in the vast online world. Your consistent delivery of high-quality content is admirable. Thank you for always going above and beyond in providing valuable insights. Keep up the fantastic work!
I couldn’t agree more with the insightful points you’ve articulated in this article. Your profound knowledge on the subject is evident, and your unique perspective adds an invaluable dimension to the discourse. This is a must-read for anyone interested in this topic.
I’d like to express my heartfelt appreciation for this enlightening article. Your distinct perspective and meticulously researched content bring a fresh depth to the subject matter. It’s evident that you’ve invested a great deal of thought into this, and your ability to articulate complex ideas in such a clear and comprehensible manner is truly commendable. Thank you for generously sharing your knowledge and making the process of learning so enjoyable.
Your unique approach to addressing challenging subjects is like a breath of fresh air. Your articles stand out with their clarity and grace, making them a pure joy to read. Your blog has now become my go-to source for insightful content.
One thing I want to discuss is that fat reduction plan fast can be carried out by the correct diet and exercise. Your size not simply affects appearance, but also the quality of life. Self-esteem, despression symptoms, health risks, and also physical abilities are disturbed in excess weight. It is possible to just make everything right and at the same time having a gain. If this happens, a condition may be the reason. While excessive food rather than enough body exercise are usually to blame, common medical ailments and widely used prescriptions can greatly increase size. Thanks alot : ) for your post in this article.
buy cheap generic propranolol motrin 600mg usa cheap plavix 75mg
Been relying on them for years, and they never disappoint. https://mexicanpharmonline.shop/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexican rx online [url=https://mexicanpharmonline.shop/#]medicines mexico[/url] medication from mexico pharmacy
In a world where trustworthy information is more crucial than ever, your dedication to research and the provision of reliable content is truly commendable. Your commitment to accuracy and transparency shines through in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online realm.
In a world where trustworthy information is more crucial than ever, your dedication to research and the provision of reliable content is truly commendable. Your commitment to accuracy and transparency shines through in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online realm.
Their global medical liaisons ensure top-quality care. https://mexicanpharmonline.shop/# best online pharmacies in mexico
mexican mail order pharmacies [url=http://mexicanpharmonline.com/#]pharmacy in mexico[/url] mexico drug stores pharmacies
nortriptyline 25mg without prescription brand paracetamol 500 mg order paracetamol 500mg pill
Global expertise that’s palpable with every service. https://mexicanpharmonline.com/# п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
mexican pharmaceuticals online [url=https://mexicanpharmonline.shop/#]medicines mexico[/url] medication from mexico pharmacy
In a world where trustworthy information is more crucial than ever, your dedication to research and the provision of reliable content is truly commendable. Your commitment to accuracy and transparency shines through in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online realm.
I wanted to take a moment to express my gratitude for the wealth of valuable information you provide in your articles. Your blog has become a go-to resource for me, and I always come away with new knowledge and fresh perspectives. I’m excited to continue learning from your future posts.
order xenical 60mg online buy mesalamine cheap order generic diltiazem 180mg
https://indiapharmacy24.pro/# Online medicine home delivery
In a world where trustworthy information is more crucial than ever, your dedication to research and the provision of reliable content is truly commendable. Your commitment to accuracy and transparency shines through in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online realm.
Your unique approach to addressing challenging subjects is like a breath of fresh air. Your articles stand out with their clarity and grace, making them a pure joy to read. Your blog has now become my go-to source for insightful content.
https://indiapharmacy24.pro/# online pharmacy india
buy cheap generic medex maxolon price buy metoclopramide 10mg for sale
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You obviously know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your blog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
https://stromectol24.pro/# cheap stromectol
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain good points in options also.
Spot on with this write-up, I actually suppose this website wants far more consideration. I?ll in all probability be once more to learn much more, thanks for that info.
Hi there, simply become aware of your blog thru Google, and located that it is truly informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels. I will be grateful in case you continue this in future. Many folks might be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
https://indiapharmacy24.pro/# best india pharmacy
Hey very nice blog!! Man .. Beautiful .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds also?I’m happy to find a lot of useful information here in the post, we need develop more techniques in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
cost astelin order zovirax 800mg pill buy irbesartan medication
http://www.thebudgetart.com is trusted worldwide canvas wall art prints & handmade canvas paintings online store. Thebudgetart.com offers budget price & high quality artwork, up-to 50 OFF, FREE Shipping USA, AUS, NZ & Worldwide Delivery.
I’m not sure exactly why but this site is loading extremely slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
Thanks for the useful information on credit repair on this excellent web-site. A few things i would offer as advice to people is always to give up a mentality that they’ll buy currently and pay later. Being a society all of us tend to try this for many things. This includes vacations, furniture, plus items we’d like. However, you should separate your own wants out of the needs. When you are working to fix your credit score make some trade-offs. For example you can shop online to economize or you can click on second hand merchants instead of costly department stores pertaining to clothing.
http://valtrex.auction/# valtrex generic otc
famotidine 40mg brand buy generic famotidine for sale order prograf 1mg without prescription
Terrific paintings! This is the type of info that are supposed to be shared across the internet. Shame on Google for not positioning this put up upper! Come on over and visit my site . Thanks =)
I think one of your commercials triggered my web browser to resize, you may well want to put that on your blacklist.
buy minocycline 100 mg tablets: stromectol over the counter – ivermectin medicine
info@purwell.com
I’d also like to state that most of those who find themselves devoid of health insurance usually are students, self-employed and people who are unemployed. More than half in the uninsured are really under the age of Thirty-five. They do not feel they are requiring health insurance simply because they’re young plus healthy. Their particular income is generally spent on houses, food, as well as entertainment. A lot of people that do represent the working class either entire or part time are not supplied insurance by means of their jobs so they move without due to rising cost of health insurance in america. Thanks for the thoughts you discuss through this website.
can you order valtrex online: valtrex coupon canada – buy valtrex pills online
nexium cheap buy esomeprazole online order topiramate 200mg online
I?ve been exploring for a little bit for any high quality articles or blog posts on this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this web site. Reading this info So i?m happy to convey that I’ve an incredibly good uncanny feeling I discovered exactly what I needed. I most certainly will make certain to don?t forget this web site and give it a glance regularly.
cialis for sale [url=https://cialis.foundation/#]Cialis 20mg price[/url] Cialis 20mg price in USA
buy allopurinol 300mg without prescription buy generic rosuvastatin for sale buy crestor 10mg pill
https://talibf604bri7.wikinewspaper.com/user
https://viagra.eus/# cheap viagra
Thanks for discussing your ideas. A very important factor is that learners have an alternative between government student loan and also a private education loan where its easier to opt for student loan consolidation than with the federal student loan.
http://kamagra.icu/# Kamagra Oral Jelly
http://cialis.foundation/# Buy Tadalafil 10mg
Kamagra tablets [url=https://kamagra.icu/#]buy Kamagra[/url] Kamagra 100mg
https://griffinq2738.newbigblog.com/28359290/the-single-best-strategy-to-use-for-chinese-medicine-blood-pressure
https://donovan2p890.blogsumer.com/22861457/the-chinese-medicine-journal-diaries
http://www.mybudgetart.com.au is Australia’s Trusted Online Wall Art Canvas Prints Store. We are selling art online since 2008. We offer 2000+ artwork designs, up-to 50 OFF store-wide, FREE Delivery Australia & New Zealand, and World-wide shipping to 50 plus countries.
buy sumatriptan no prescription buy avodart 0.5mg without prescription avodart over the counter
viagra without prescription [url=http://viagra.eus/#]generic sildenafil[/url] Cheap generic Viagra online
buspirone 5mg price buy cheap generic buspirone buy generic cordarone over the counter
I’m not sure why but this site is loading very slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
https://kamagra.icu/# cheap kamagra
https://mikhails246pon7.ouyawiki.com/user
https://stanleyt232uka0.bimmwiki.com/user
Levitra 10 mg best price [url=http://levitra.eus/#]Levitra online pharmacy[/url] Levitra 20 mg for sale
https://jared4gr14.blogdigy.com/the-single-best-strategy-to-use-for-chinese-medicine-classes-36557963
https://marjaneyx582lvd5.wikilima.com/user
https://beckettswt01.blog2learn.com/70601816/business-trip-management-system-for-dummies
https://dallas76534.bloggerswise.com/28595408/the-basic-principles-of-chinese-medicine-body-types
https://garrett0xi92.activoblog.com/23006466/the-smart-trick-of-chinese-medicine-journal-that-no-one-is-discussing
https://juliat483cxr1.wikibuysell.com/user
https://damien9f456.verybigblog.com/22864230/a-simple-key-for-chinese-medicine-cooker-unveiled
https://maryu133gda2.wikijm.com/user
http://kamagra.icu/# cheap kamagra
Buy Cialis online [url=http://cialis.foundation/#]Cialis 20mg price[/url] Cheap Cialis
https://hector2yr04.blogsvila.com/23033985/the-single-best-strategy-to-use-for-chinese-medicine-classes
https://georgesb186vdi0.blogpayz.com/profile
domperidone sale domperidone 10mg pills tetracycline pills
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your blogs really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your site to come back down the road. Many thanks
https://devinv1233.estate-blog.com/22889408/the-best-side-of-chinese-medicine-basics
https://socialwebnotes.com/story1094972/5-easy-facts-about-chinese-medical-massage-described
https://yxzbookmarks.com/story15832015/5-simple-techniques-for-massage-business-tips
Pretty portion of content. I simply stumbled upon your web site and in accession capital to say that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I?ll be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you get entry to constantly rapidly.
I do agree with all the ideas you’ve presented in your post. They’re very convincing and will certainly work. Still, the posts are too short for starters. Could you please extend them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.
buy Levitra over the counter [url=https://levitra.eus/#]Cheap Levitra online[/url] Vardenafil price
Some genuinely select content on this site, saved to favorites.
http://kamagra.icu/# cheap kamagra
https://quentinl900vqj5.onzeblog.com/profile
https://steveb579vvt9.robhasawiki.com/user
https://marcol78sp.ageeksblog.com/22787018/korean-massage-bed-options
https://sidneyw112yun6.hazeronwiki.com/user
https://andre46u9v.bloggerbags.com/27744225/the-basic-principles-of-chinese-medicine-body-types
https://kamagra.icu/# Kamagra 100mg price
Good day very nice site!! Man .. Excellent .. Superb .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds also?I’m satisfied to search out a lot of helpful info right here in the submit, we want develop more strategies in this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
I?m no longer certain where you are getting your information, however great topic. I must spend some time studying more or understanding more. Thank you for wonderful info I used to be searching for this info for my mission.
buy tamsulosin 0.4mg where to buy flomax without a prescription brand simvastatin 10mg
Cialis 20mg price in USA [url=http://cialis.foundation/#]Cialis 20mg price in USA[/url] buy cialis pill
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your blog. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more enjoyable for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create your theme? Great work!
https://martinh55h3.ageeksblog.com/22697578/facts-about-thailand-massage-revealed
https://hansl909nfw9.iamthewiki.com/user
https://extrabookmarking.com/story15833087/a-secret-weapon-for-thailand-massage-types
I have learned some new elements from your internet site about pcs. Another thing I have always considered is that laptop computers have become a specific thing that each household must have for many reasons. They supply you with convenient ways in which to organize the home, pay bills, go shopping, study, pay attention to music and in some cases watch television shows. An innovative technique to complete these types of tasks is a computer. These desktops are mobile, small, potent and transportable.
I like the valuable information you provide on your articles. I will bookmark your weblog and take a look at again right here regularly. I am fairly sure I will learn a lot of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
academia writing practice essay writing online essay writing assistance
https://kamagra.icu/# super kamagra
https://julius3dz49.thezenweb.com/the-smart-trick-of-chinese-medicine-chi-that-nobody-is-discussing-60004919
https://collin184p3.blogtov.com/3331188/massage-chinese-translation-options
https://titus68y1a.blogolize.com/not-known-details-about-chinese-medicine-cupping-62068556
https://galileop984kri3.illawiki.com/user
indianpharmacy com: india pharmacy mail order – buy medicines online in india indiapharmacy.pro
I haven?t checked in here for some time since I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are great quality so I guess I will add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
https://nealeh802dbz2.yourkwikimage.com/user
https://gregoryt9986.thekatyblog.com/22864170/chinese-medicine-basics-options
https://josuei667o.blog-mall.com/23052910/the-single-best-strategy-to-use-for-korean-massage-chair-brands
order aldactone 25mg sale aldactone 25mg cheap propecia order online
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: mexico drug stores pharmacies – purple pharmacy mexico price list mexicanpharmacy.company
Hello there, I discovered your site by the use of Google at the same time as searching for a related matter, your website got here up, it looks good. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
https://zaneu3692.glifeblog.com/22870461/the-basic-principles-of-chinese-medicine-books
https://mario6zayw.topbloghub.com/28624536/not-known-facts-about-korean-massage-near-19002
https://danteuabb34556.mybjjblog.com/how-us-massage-service-can-save-you-time-stress-and-money-36403928
https://andrex2344.blog5.net/64093467/little-known-facts-about-chinese-medicine-acupuncture-points
https://eduardo6ef45.blogdon.net/top-chinese-medicine-classes-secrets-38846019
best online pharmacy india: buy prescription drugs from india – india pharmacy mail order indiapharmacy.pro
order aurogra sildenafil pills 100mg purchase estradiol online cheap
http://indiapharmacy.pro/# Online medicine order indiapharmacy.pro
https://ermab926yis1.law-wiki.com/user
https://socialupme.com/story1241794/a-simple-key-for-chinese-medicine-basics-unveiled
https://socialicus.com/story1130184/not-known-factual-statements-about-chinese-medicine-basics
purple pharmacy mexico price list: mexico drug stores pharmacies – best online pharmacies in mexico mexicanpharmacy.company
top 10 online pharmacy in india: indianpharmacy com – top 10 pharmacies in india indiapharmacy.pro
Howdy! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I really enjoy reading your blog posts. Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same subjects? Many thanks!
Thanks for your useful article. Other thing is that mesothelioma is generally a result of the inhalation of materials from asbestos fiber, which is a positivelly dangerous material. Its commonly seen among workers in the construction industry who’ve long contact with asbestos. It can also be caused by moving into asbestos insulated buildings for long periods of time, Inherited genes plays a huge role, and some persons are more vulnerable on the risk compared to others.
cost fluconazole 100mg buy ampicillin no prescription order cipro 500mg sale
I have learn several good stuff here. Definitely price bookmarking for revisiting.
I wonder how a lot effort you set to create this sort of fantastic informative web site.
onlinecanadianpharmacy: my canadian pharmacy – canadian valley pharmacy canadapharmacy.guru
drugs from canada: canadian drug pharmacy – 77 canadian pharmacy canadapharmacy.guru
https://ferdinandd677nie2.qodsblog.com/profile
https://jasper50482.blogdemls.com/22869057/facts-about-chinese-medicine-chart-revealed
https://thomasw627sqp2.bloggerbags.com/27776266/not-known-facts-about-chinese-medicine-body-map
buying prescription drugs in mexico online: pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa – mexico drug stores pharmacies mexicanpharmacy.company
It is my belief that mesothelioma is usually the most dangerous cancer. It contains unusual traits. The more I look at it a lot more I am assured it does not respond like a true solid flesh cancer. In the event mesothelioma is a rogue viral infection, then there is the probability of developing a vaccine and offering vaccination for asbestos open people who are at high risk connected with developing long run asbestos relevant malignancies. Thanks for expressing your ideas on this important health issue.
best india pharmacy: pharmacy website india – best india pharmacy indiapharmacy.pro
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies [url=http://mexicanpharmacy.company/#]medicine in mexico pharmacies[/url] pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexicanpharmacy.company
https://zaneafebz.angelinsblog.com/22816543/a-review-of-thailand-massage-bangkok
https://ellenm220xxt8.hamachiwiki.com/user
https://emilianoz1097.idblogz.com/23132667/new-step-by-step-map-for-chinese-medicine-chart
flagyl medication buy generic cephalexin buy cephalexin generic
Thank you for any other informative website. Where else may I am getting that kind of info written in such a perfect way? I have a challenge that I am simply now operating on, and I have been at the glance out for such information.
mexican pharmaceuticals online: mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs mexicanpharmacy.company
mexico drug stores pharmacies: buying prescription drugs in mexico – pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexicanpharmacy.company
medicine in mexico pharmacies [url=https://mexicanpharmacy.company/#]buying prescription drugs in mexico online[/url] mexican rx online mexicanpharmacy.company
You are my intake, I own few blogs and occasionally run out from post :). “Analyzing humor is like dissecting a frog. Few people are interested and the frog dies of it.” by E. B. White.
https://mario0wj81.blogsumer.com/22864461/top-guidelines-of-chinese-medicine-cooker
https://laneb1741.laowaiblog.com/22806086/not-known-facts-about-chinese-medicine-clinic
online pharmacy india: world pharmacy india – top 10 pharmacies in india indiapharmacy.pro
Thanks for discussing your ideas right here. The other element is that if a problem comes up with a laptop or computer motherboard, persons should not go ahead and take risk regarding repairing it themselves for if it is not done properly it can lead to irreparable damage to the whole laptop. It is almost always safe to approach any dealer of a laptop for the repair of that motherboard. They have got technicians with an experience in dealing with notebook computer motherboard troubles and can get the right prognosis and perform repairs.
order tretinoin gel online cheap tadalis 10mg buy avana 200mg online
canada drugs online: canadian pharmacy world reviews – legit canadian pharmacy canadapharmacy.guru
Thanks for your write-up on this weblog. From my very own experience, there are occassions when softening right up a photograph might provide the photographer with a little an artistic flare. More often than not however, that soft blur isn’t just what you had as the primary goal and can sometimes spoil a normally good photograph, especially if you thinking about enlarging this.
cleocin 150mg canada erythromycin pills best ed drugs
canadian pharmacy checker: drugs from canada – canadian pharmacy sarasota canadapharmacy.guru
http://doxycycline.sbs/# doxycycline tablets
where can i buy generic clomid without prescription [url=https://clomid.sbs/#]where can i buy clomid pills[/url] cheap clomid without dr prescription
http://clomid.sbs/# can you buy clomid prices
Thank you for the good writeup. It in truth was once a entertainment account it. Glance complex to more introduced agreeable from you! By the way, how can we keep in touch?
https://cruzq0370.ja-blog.com/22977215/new-step-by-step-map-for-chinese-medicine-body-chart
https://zbigniewg780xvu9.empirewiki.com/user
https://andresw1098.educationalimpactblog.com/44930438/5-easy-facts-about-chinese-medicine-blood-deficiency-described
https://prednisone.digital/# prednisone cream brand name
purchase tadacip without prescription cost diclofenac 50mg order indomethacin 75mg without prescription
tamoxifen 20mg without prescription order budesonide generic symbicort medication
Thanks for your publication on this blog site. From my personal experience, often times softening right up a photograph may well provide the digital photographer with a dose of an imaginative flare. Sometimes however, the soft cloud isn’t precisely what you had at heart and can quite often spoil an otherwise good snapshot, especially if you consider enlarging them.
http://amoxil.world/# amoxicillin medicine
10mg prednisone daily [url=http://prednisone.digital/#]buy prednisone online no prescription[/url] prednisone best price
http://prednisone.digital/# canadian online pharmacy prednisone
https://simonf1471.blogripley.com/23151722/not-known-facts-about-chinese-medicine-body-map
http://prednisone.digital/# order prednisone
buying cheap clomid [url=http://clomid.sbs/#]how to buy generic clomid no prescription[/url] cost of cheap clomid without a prescription
http://doxycycline.sbs/# order doxycycline online
I think one of your advertisings caused my web browser to resize, you may well want to put that on your blacklist.
https://doxycycline.sbs/# doxycycline without prescription
can you get clomid price [url=http://clomid.sbs/#]where can i get cheap clomid for sale[/url] get cheap clomid
https://propecia.sbs/# generic propecia price
buy terbinafine 250mg lamisil 250mg cheap recommended you read
cheap cefuroxime buy generic methocarbamol oral methocarbamol
https://propecia.sbs/# buying cheap propecia without a prescription
cost of cheap propecia tablets [url=http://propecia.sbs/#]cost cheap propecia no prescription[/url] buy generic propecia without prescription
https://amoxil.world/# how much is amoxicillin
https://propecia.sbs/# get generic propecia without rx
buy prednisone online canada [url=https://prednisone.digital/#]prednisone 12 mg[/url] prednisone 20mg by mail order
https://doxycycline.sbs/# buy doxycycline without prescription uk
Thanks for your blog post. I would also love to say a health insurance agent also works best for the benefit of the particular coordinators of your group insurance policy. The health insurance broker is given an index of benefits searched for by someone or a group coordinator. What any broker can is find individuals as well as coordinators which will best fit those demands. Then he reveals his ideas and if each party agree, the broker formulates binding agreement between the two parties.
cost generic propecia online: cost propecia online – propecia pill
https://amoxil.world/# amoxicillin 875 125 mg tab
buy doxycycline 100mg [url=http://doxycycline.sbs/#]doxycycline online[/url] doxy
http://doxycycline.sbs/# order doxycycline 100mg without prescription
http://prednisone.digital/# prednisone canada
amoxicillin over counter [url=https://amoxil.world/#]amoxicillin brand name[/url] amoxicillin cost australia
trazodone 100mg sale buy sildenafil 100mg clindac a cheap
Thanks for the points shared on your own blog. Another thing I would like to mention is that weight-loss is not all about going on a celebrity diet and trying to shed as much weight as possible in a set period of time. The most effective way to lose weight is by having it gradually and obeying some basic suggestions which can make it easier to make the most from the attempt to shed weight. You may be aware and be following these tips, nonetheless reinforcing knowledge never does any damage.
https://mexicopharm.shop/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
http://withoutprescription.guru/# mexican pharmacy without prescription
best online pharmacies in mexico [url=http://mexicopharm.shop/#]mexican drugstore online[/url] mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
https://indiapharm.guru/# best india pharmacy
https://canadapharm.top/# online canadian drugstore
mexico drug stores pharmacies: medication from mexico pharmacy – mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
cheap term papers my experience in college essay generic cefixime 200mg
https://edpills.icu/# best over the counter ed pills
best canadian pharmacy to buy from: Accredited Canadian and International Online Pharmacies – ordering drugs from canada
http://withoutprescription.guru/# buy prescription drugs without doctor
top rated ed pills: ed pills online – treatments for ed
indian pharmacy: top 10 online pharmacy in india – top online pharmacy india
http://tty28.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=44969
http://edpills.icu/# drugs for ed
cheap essay help teach me how to write an essay play online blackjack for real money
buy amoxicillin 500mg for sale buy clarithromycin 500mg clarithromycin 250mg sale
you’ve got an excellent weblog right here! would you wish to make some invite posts on my blog?
buy erection pills: medication for ed dysfunction – п»їerectile dysfunction medication
Thanks for your information on this blog. One particular thing I would wish to say is that often purchasing gadgets items through the Internet is not something new. In truth, in the past several years alone, the marketplace for online electronic products has grown a great deal. Today, you’ll find practically any type of electronic tool and product on the Internet, ranging from cameras as well as camcorders to computer elements and game playing consoles.
http://indiapharm.guru/# reputable indian online pharmacy
mexican pharmaceuticals online: buying prescription drugs in mexico – reputable mexican pharmacies online
https://withoutprescription.guru/# viagra without doctor prescription
Would you be enthusiastic about exchanging hyperlinks?
cheap kamagra: buy kamagra online usa – cheap kamagra
buy rocaltrol tablets trandate 100 mg for sale brand tricor
order catapres 0.1mg online cheap buy catapres 0.1mg generic tiotropium bromide pill
erectile dysfunction medications: erectile dysfunction medicines – generic ed pills
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! By the way, how could we communicate?
http://levitra.icu/# Buy Levitra 20mg online
buy Levitra over the counter: Levitra generic best price – Buy Levitra 20mg online
http://df123w.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=33378
https://levitra.icu/# Vardenafil online prescription
https://www.adsoftheworld.com/users/83229583-adc9-4311-999c-dbca328afe2c
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to assert that I acquire actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
most common medication prescribed acne dermatologist recommended acne medication buy oxcarbazepine 300mg sale
http://tadalafil.trade/# tadalafil tablet buy online
Good day! Would you mind if I share your blog with my zynga group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thank you
oral minomycin ropinirole 1mg tablet ropinirole 2mg drug
generic sildenafil us: sildenafil citrate 50mg tab – sildenafil fast delivery
http://edpills.monster/# treatment of ed
https://doxycycline.forum/# doxycycline for sale online uk
prescription drug prices lisinopril [url=http://lisinopril.auction/#]Over the counter lisinopril[/url] lisinopril medication generic
Good ? I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs and related info ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, website theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Excellent task..
https://azithromycin.bar/# zithromax prescription
order uroxatral online natural substitute for famotidine arthritis medication without stomach upset
where can i buy cipro online [url=http://ciprofloxacin.men/#]buy ciprofloxacin online[/url] ciprofloxacin over the counter
https://azithromycin.bar/# zithromax for sale online
cost femara 2.5mg letrozole 2.5mg for sale abilify 30mg canada
how to get amoxicillin: purchase amoxicillin online – how to buy amoxycillin
lisinopril 5 mg daily [url=http://lisinopril.auction/#]Buy Lisinopril 20 mg online[/url] prinivil 5 mg tablets
SightCare works by targeting the newly discovered root cause of vision impairment. According to research studies carried out by great universities and research centers, this root cause is a decrease in the antioxidant levels in the body.
https://doxycycline.forum/# where can i buy doxycycline over the counter
cost of generic zithromax: buy cheap generic zithromax – zithromax 500 mg lowest price pharmacy online
amoxicillin 775 mg [url=https://amoxicillin.best/#]buy amoxil[/url] amoxicillin 500mg price in canada
sleeping pills non prescription uk fda approved hair growth medication heathing lost pills
very nice post, i definitely love this website, carry on it
http://doxycycline.forum/# buy doxycycline pills online
zithromax 500 mg lowest price drugstore online [url=http://azithromycin.bar/#]zithromax over the counter canada[/url] zithromax generic price
You actually make it appear really easy along with your presentation however I in finding this topic to be actually one thing that I feel I might never understand. It sort of feels too complicated and very vast for me. I’m having a look forward for your subsequent put up, I will attempt to get the dangle of it!
order provera buy medroxyprogesterone generic order hydrochlorothiazide 25mg pill
nick.difrancesco@purwell.com
https://lisinopril.auction/# rx lisinopril
http://mexicopharmacy.store/# best online pharmacies in mexico
best online pharmacies in mexico: mexican pharmacy – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
fda approved smoking cessation medications supplements for stronger bones strongest painkillers list
http://canadiandrugs.store/# canadian pharmacy drugs online
india pharmacy mail order: mail order pharmacy india – india pharmacy
periactin online order cyproheptadine generic order nizoral sale
https://buydrugsonline.top/# canadian pharmacy meds
canada medicine: cheap drugs online – canadian world pharmacy
how are antiviral drugs used cheapest long term asthma cortocosteroid diabetic pills type 1
What’s up Dear, are you truly visiting this web page regularly, if so
after that you will absolutely obtain nice know-how.
Buy Actiflow 78% off USA (Official). Actiflow is a natural and effective leader in prostate health supplements
Aizen Power is a dietary supplement for male enhancement sexual health that is designed to help enhance men’s performance and improve overall health.
Boostaro is a natural health formula for men that aims to improve health.
ErecPrime is a natural male enhancement support that helps with boosting your stamina and virility in addition to enhancing pleasure.
Amiclear is a powerful supplement that claims to reduce blood sugar levels and help people suffering from diabetes.
Cortexi is a natural hearing support aid that has been used by thousands of people around the globe.
Dentitox Pro is an All-Natural Liquid Oral Hygiene Supplement Consists Unique Combination Of Vitamins And Plant Extracts To Support The Health Of Gums
Heya i?m for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It really useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and aid others like you helped me.
Quietum Plus is a 100% natural supplement designed to address ear ringing and other hearing issues. This formula uses only the best in class and natural ingredients to achieve desired results.
buy cymbalta 20mg modafinil online buy provigil oral
EndoPeak is a natural energy-boosting formula designed to improve men’s stamina, energy levels, and overall health.
Introducing Claritox Pro, a natural supplement designed to help you maintain your balance and prevent dizziness.
SightCare ingredients have the ability to promote the communication processes between the eye and the brain. They tend to enhance the production of chemical compounds that help in creating neurotransmitters. By getting these neurotransmitters to perform better, the ingredients solidify the connection between the eyes and the brain.
Fast Lean Pro is a herbal supplement that tricks your brain into imagining that you’re fasting and helps you maintain a healthy weight no matter when or what you eat.
GlucoTru Diabetes Supplement is a natural blend of various natural components.
Eye Fortin is a strong vision-supporting formula that supports healthy eyes and strong eyesight.
best online site for diflucan list of high blood pressure meds alphabetical high blood pressure medication refill
Hello i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anywhere, when i read this article i thought
i could also make comment due to this brilliant post.
Buy Metanail Serum Pro USA official website. Say goodbye to nail and foot woes and hello to healthy, happy hands and feet with Metanail Serum Pro
paxlovid pill https://paxlovid.club/# paxlovid cost without insurance
FitSpresso is a special supplement that makes it easier for you to lose weight. It has natural ingredients that help your body burn fat better.
NeuroPure is a breakthrough dietary formula designed to alleviate neuropathy, a condition that affects a significant number of individuals with diabetes.
Nervogen Pro is a dietary formula that contains 100% natural ingredients. The powerful blend of ingredients claims to support a healthy nervous system. Each capsule includes herbs and antioxidants that protect the nerve against damage and nourishes the nerves with the required nutrients. Order Your Nervogen Pro™ Now!
Buy neurodrine memory supplement (Official). The simplest way to maintain a steel trap memory
Thanks for revealing your ideas. I might also like to say that video games have been at any time evolving. Modern tools and innovations have made it easier to create reasonable and fun games. Most of these entertainment video games were not really sensible when the concept was being tried out. Just like other forms of technological innovation, video games too have had to develop by means of many years. This is testimony towards the fast development of video games.
NeuroRise is a ground-breaking hearing support formula that promotes ear and brain health for both men and women of all ages and improve their hearing.
http://www.spotnewstrend.com is a trusted latest USA News and global news provider. Spotnewstrend.com website provides latest insights to new trends and worldwide events. So keep visiting our website for USA News, World News, Financial News, Business News, Entertainment News, Celebrity News, Sport News, NBA News, NFL News, Health News, Nature News, Technology News, Travel News.
ProDentim is an innovative dental health supplement that boasts of a unique blend of 3.5 billion probiotics and essential nutrients
Prostadine works really well because it’s made from natural things. The people who made it spent a lot of time choosing these natural things to help your mind work better without any bad effects.
magnificent points altogether, you just gained a new reader. What may you recommend in regards to your put up that you simply made some days in the past? Any sure?
ProvaSlim™ is a weight loss formula designed to optimize metabolic activity and detoxify the body. It specifically targets metabolic dysfunction
VidaCalm is an herbal supplement that claims to permanently silence tinnitus.
Alpha Tonic daily testosterone booster for energy and performance. Convenient powder form ensures easy blending into drinks for optimal absorption.
Neurozoom is one of the best supplements out on the market for supporting your brain health and, more specifically, memory functions.
most prescribed medication for ulcers uti over counter treatment uti med over the counter
SonoVive™ is a 100% natural hearing supplement by Sam Olsen made with powerful ingredients that help heal tinnitus problems and restore your hearing.
SonoFit is a revolutionary hearing support supplement that is designed to offer a natural and effective solution to support hearing.
SynoGut supplement that restores your gut lining and promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria.
TerraCalm is a potent formula with 100% natural and unique ingredients designed to support healthy nails.
TonicGreens flushes away the harmful elements from your body, leaving you feeling refreshed and revitalized.
Tropislim, is an all-natural dietary supplement. It promotes healthy weight loss through a proprietary blend of tropical plants and nutrients.
This is the proper blog for anybody who desires to seek out out about this topic. You understand so much its virtually hard to argue with you (not that I really would need?HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a subject thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just nice!
ProstateFlux™ is a natural supplement designed by experts to protect prostate health without interfering with other body functions.
Pineal XT™ is a dietary supplement crafted from entirely organic ingredients, ensuring a natural formulation.
obviously like your website but you have to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I to find it very troublesome to tell the truth nevertheless I will definitely come again again.
can i order generic clomid for sale: Buy Clomid Shipped From Canada – can i buy generic clomid online
What sets this blog apart from others is its ability to provide a truly unique perspective on a wide range of topics. The author has a talent for presenting information in a way that is both accessible and engaging. I appreciate the depth of research that goes into each post, as well as the author’s ability to provide insights that are both informative and thought-provoking. This blog has become a go-to resource for me, and I highly recommend it to anyone who values substantive and interesting content.
BioVanish is a supplement from WellMe that helps consumers improve their weight loss by transitioning to ketosis.
GlucoBerry is a unique supplement that offers an easy and effective way to support balanced blood sugar levels.
prednisone 10mg cheap deltasone buy online order amoxil 250mg without prescription
Joint Genesis is a supplement from BioDynamix that helps consumers to improve their joint health to reduce pain.
MenoRescue™ is a women’s health dietary supplement formulated to assist them in overcoming menopausal symptoms.
acquisto farmaci con ricetta: Farmacie a milano che vendono cialis senza ricetta – comprare farmaci online con ricetta
https://farmaciait.pro/# acquisto farmaci con ricetta
acquisto farmaci con ricetta: avanafil prezzo – farmacie on line spedizione gratuita
online doctor birth control birth control pills online free best pills for semen volume
farmacia senza ricetta recensioni: sildenafil prezzo – viagra generico in farmacia costo
viagra acquisto in contrassegno in italia: sildenafil prezzo – viagra consegna in 24 ore pagamento alla consegna
comprare farmaci online con ricetta: kamagra gel – farmacie on line spedizione gratuita
I’m really inspired along with your writing skills as well as with the structure for your weblog. Is that this a paid subject or did you modify it yourself? Either way keep up the excellent high quality writing, it is rare to see a nice weblog like this one these days..
migliori farmacie online 2023: dove acquistare cialis online sicuro – farmacie on line spedizione gratuita
One more thing. In my opinion that there are several travel insurance web-sites of respectable companies that let you enter holiday details and have you the estimates. You can also purchase this international holiday insurance policy on the net by using your credit card. Everything you should do is to enter your current travel specifics and you can understand the plans side-by-side. Only find the plan that suits your capacity to pay and needs and then use your credit card to buy them. Travel insurance online is a good way to check for a respectable company with regard to international travel cover. Thanks for giving your ideas.
ortexi is a 360° hearing support designed for men and women who have experienced hearing loss at some point in their lives.
viagra naturale in farmacia senza ricetta: viagra online siti sicuri – viagra generico sandoz
farmacia online miglior prezzo: farmacia online più conveniente – farmacie online affidabili
http://farmaciait.pro/# farmacie online sicure
Usually I don’t learn post on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up very forced me to check out and do it! Your writing style has been surprised me. Thank you, very great article.
comprare farmaci online all’estero: farmacia online miglior prezzo – comprare farmaci online all’estero
Amiclear is a blood sugar support formula that’s perfect for men and women in their 30s, 40s, 50s, and even 70s.
buy zithromax tablets buy azithromycin 500mg generic gabapentin canada
SharpEar™ is a 100% natural ear care supplement created by Sam Olsen that helps to fix hearing loss
farmacia online migliore: avanafil – farmacie online autorizzate elenco
farmacia online migliore: kamagra oral jelly – farmacia online miglior prezzo
https://avanafilit.icu/# migliori farmacie online 2023
Hiya, I’m really glad I have found this information. Today bloggers publish only about gossips and web and this is actually irritating. A good blog with exciting content, this is what I need. Thanks for keeping this website, I’ll be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Cant find it.
Thank you for sharing your info. I really appreciate your efforts and I will be waiting for your
further post thanks once again.
viagra consegna in 24 ore pagamento alla consegna: sildenafil prezzo – viagra online spedizione gratuita
https://sildenafilit.bid/# cerco viagra a buon prezzo
farmacie on line spedizione gratuita: farmacia online miglior prezzo – farmacia online più conveniente
I’ve been browsing on-line more than 3 hours nowadays, but I by no means discovered any fascinating article like yours. It?s beautiful worth enough for me. In my view, if all web owners and bloggers made excellent content material as you did, the web shall be a lot more useful than ever before.
farmacia 24h [url=https://tadalafilo.pro/#]comprar cialis original[/url] farmacias online seguras
http://farmacia.best/# farmacia online barata
purchase ursodiol zyban 150 mg sale order cetirizine 5mg pill
farmacia online internacional [url=https://tadalafilo.pro/#]Cialis precio[/url] farmacia envГos internacionales
This article resonated with me on a personal level. Your ability to connect with your audience emotionally is commendable. Your words are not only informative but also heartwarming. Thank you for sharing your insights.
In a world where trustworthy information is more crucial than ever, your dedication to research and the provision of reliable content is truly commendable. Your commitment to accuracy and transparency shines through in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online realm.
I’m genuinely impressed by how effortlessly you distill intricate concepts into easily digestible information. Your writing style not only imparts knowledge but also engages the reader, making the learning experience both enjoyable and memorable. Your passion for sharing your expertise shines through, and for that, I’m deeply grateful.
Do you mind if I quote a few of your articles as long as I provide credit and sources back to your blog? My blog is in the exact same niche as yours and my visitors would truly benefit from a lot of the information you provide here. Please let me know if this ok with you. Many thanks!
sildenafilo sandoz 100 mg precio [url=http://sildenafilo.store/#]comprar viagra[/url] comprar sildenafilo cinfa 100 mg espaГ±a
I wanted to take a moment to express my gratitude for the wealth of invaluable information you consistently provide in your articles. Your blog has become my go-to resource, and I consistently emerge with new knowledge and fresh perspectives. I’m eagerly looking forward to continuing my learning journey through your future posts.
Your unique approach to addressing challenging subjects is like a breath of fresh air. Your articles stand out with their clarity and grace, making them a pure joy to read. Your blog has now become my go-to source for insightful content.
I wanted to take a moment to express my gratitude for the wealth of invaluable information you consistently provide in your articles. Your blog has become my go-to resource, and I consistently emerge with new knowledge and fresh perspectives. I’m eagerly looking forward to continuing my learning journey through your future posts.
https://kamagraes.site/# farmacia online madrid
The subsequent time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I imply, I know it was my choice to learn, however I really thought youd have something fascinating to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you may fix in case you werent too busy searching for attention.
order strattera online cheap buy generic strattera for sale buy sertraline cheap
comprar viagra en espaГ±a amazon [url=http://sildenafilo.store/#]viagra precio[/url] se puede comprar viagra sin receta
http://sildenafilo.store/# sildenafilo 100mg precio farmacia
Your enthusiasm for the subject matter radiates through every word of this article; it’s contagious! Your commitment to delivering valuable insights is greatly valued, and I eagerly anticipate more of your captivating content. Keep up the exceptional work!
Your storytelling prowess is nothing short of extraordinary. Reading this article felt like embarking on an adventure of its own. The vivid descriptions and engaging narrative transported me, and I eagerly await to see where your next story takes us. Thank you for sharing your experiences in such a captivating manner.
In a world where trustworthy information is more important than ever, your commitment to research and providing reliable content is truly commendable. Your dedication to accuracy and transparency is evident in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online world.
farmacia 24h [url=https://vardenafilo.icu/#]vardenafilo sin receta[/url] farmacias online seguras
https://vardenafilo.icu/# farmacias baratas online envÃo gratis
http://tadalafilo.pro/# farmacia barata
buy escitalopram sale order escitalopram 10mg generic order revia
amoxiclav order buy serophene online clomid 100mg generic
http://tadalafilo.pro/# farmacias baratas online envÃo gratis
http://sildenafilo.store/# sildenafilo sandoz 100 mg precio
Your blog has rapidly become my trusted source of inspiration and knowledge. I genuinely appreciate the effort you invest in crafting each article. Your dedication to delivering high-quality content is apparent, and I eagerly await every new post.
Your storytelling abilities are nothing short of incredible. Reading this article felt like embarking on an adventure of its own. The vivid descriptions and engaging narrative transported me, and I can’t wait to see where your next story takes us. Thank you for sharing your experiences in such a captivating way.
I am continually impressed by your ability to delve into subjects with grace and clarity. Your articles are both informative and enjoyable to read, a rare combination. Your blog is a valuable resource, and I am sincerely grateful for it.
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an shakiness over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again as exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this increase.
https://tadalafilo.pro/# farmacia online 24 horas
farmacia online 24 horas [url=https://farmacia.best/#]farmacia online internacional[/url] farmacia online barata
http://kamagraes.site/# farmacias online seguras
https://farmacia.best/# farmacias online seguras
Your blog is a true gem in the vast expanse of the online world. Your consistent delivery of high-quality content is truly commendable. Thank you for consistently going above and beyond in providing valuable insights. Keep up the fantastic work!
Your storytelling abilities are nothing short of incredible. Reading this article felt like embarking on an adventure of its own. The vivid descriptions and engaging narrative transported me, and I can’t wait to see where your next story takes us. Thank you for sharing your experiences in such a captivating way.
I am continually impressed by your ability to delve into subjects with grace and clarity. Your articles are both informative and enjoyable to read, a rare combination. Your blog is a valuable resource, and I am sincerely grateful for it.
http://sildenafilo.store/# farmacia gibraltar online viagra
where can i buy ipratropium zyvox 600mg cost buy generic linezolid
п»їfarmacia online: Comprar Levitra Sin Receta En Espana – farmacia 24h
https://pharmacieenligne.guru/# Pharmacie en ligne pas cher
Undeniably believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the net the simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people think about worries that they just don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people could take a signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
acheter mГ©dicaments Г l’Г©tranger [url=http://levitrafr.life/#]Levitra sans ordonnance 24h[/url] Pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance
Prix du Viagra 100mg en France: Viagra homme prix en pharmacie sans ordonnance – Viagra gГ©nГ©rique pas cher livraison rapide
http://kamagrafr.icu/# Pharmacie en ligne livraison 24h
Your blog is a true gem in the vast expanse of the online world. Your consistent delivery of high-quality content is truly commendable. Thank you for consistently going above and beyond in providing valuable insights. Keep up the fantastic work!
I’m continually impressed by your ability to dive deep into subjects with grace and clarity. Your articles are both informative and enjoyable to read, a rare combination. Your blog is a valuable resource, and I’m grateful for it.
Your dedication to sharing knowledge is unmistakable, and your writing style is captivating. Your articles are a pleasure to read, and I consistently come away feeling enriched. Thank you for being a dependable source of inspiration and information.
viagra online cerca de zaragoza: sildenafilo cinfa 100 mg precio farmacia – venta de viagra a domicilio
http://viagrasansordonnance.store/# Viagra femme ou trouver
acheter medicament a l etranger sans ordonnance [url=http://cialissansordonnance.pro/#]Acheter Cialis[/url] п»їpharmacie en ligne
http://levitrafr.life/# Pharmacie en ligne pas cher
http://levitrafr.life/# Acheter médicaments sans ordonnance sur internet
comprar viagra online en andorra: farmacia gibraltar online viagra – viagra online cerca de bilbao
http://cialissansordonnance.pro/# pharmacie ouverte 24/24
pharmacie ouverte [url=http://pharmacieenligne.guru/#]Pharmacies en ligne certifiees[/url] acheter mГ©dicaments Г l’Г©tranger
acheter mГ©dicaments Г l’Г©tranger: Levitra acheter – Pharmacie en ligne fiable
levitra 10mg drug zanaflex canada order hydroxychloroquine online
https://cialissansordonnance.pro/# Pharmacie en ligne livraison gratuite
https://kamagrafr.icu/# Pharmacie en ligne livraison rapide
cost nateglinide 120 mg atacand tablet buy candesartan 16mg pills
Pharmacie en ligne pas cher [url=https://kamagrafr.icu/#]kamagra livraison 24h[/url] п»їpharmacie en ligne
https://pharmacieenligne.guru/# acheter médicaments à l’étranger
http://pharmacieenligne.guru/# Pharmacie en ligne livraison rapide
Your passion and dedication to your craft shine brightly through every article. Your positive energy is contagious, and it’s clear you genuinely care about your readers’ experience. Your blog brightens my day!
Your positivity and enthusiasm are undeniably contagious! This article brightened my day and left me feeling inspired. Thank you for sharing your uplifting message and spreading positivity among your readers.
I’m genuinely impressed by how effortlessly you distill intricate concepts into easily digestible information. Your writing style not only imparts knowledge but also engages the reader, making the learning experience both enjoyable and memorable. Your passion for sharing your expertise is unmistakable, and for that, I am deeply appreciative.
http://apotheke.company/# п»їonline apotheke
Admiring the time and energy you put into your website and in depth information you provide. It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed information. Great read! I’ve saved your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.
http://apotheke.company/# п»їonline apotheke
I wanted to take a moment to express my gratitude for the wealth of invaluable information you consistently provide in your articles. Your blog has become my go-to resource, and I consistently emerge with new knowledge and fresh perspectives. I’m eagerly looking forward to continuing my learning journey through your future posts.
This article resonated with me on a personal level. Your ability to emotionally connect with your audience is truly commendable. Your words are not only informative but also heartwarming. Thank you for sharing your insights.
I’d like to express my heartfelt appreciation for this insightful article. Your unique perspective and well-researched content bring a fresh depth to the subject matter. It’s evident that you’ve invested considerable thought into this, and your ability to convey complex ideas in such a clear and understandable way is truly commendable. Thank you for sharing your knowledge so generously and making the learning process enjoyable.
buy cenforce without prescription buy aralen 250mg generic order glucophage 1000mg online
https://cialiskaufen.pro/# versandapotheke versandkostenfrei
I’ve been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks , I will try and check back more often. How frequently you update your website?
carbamazepine usa purchase lincomycin generic buy lincomycin 500 mg pill
http://viagrakaufen.store/# In welchen europäischen Ländern ist Viagra frei verkäuflich
Your dedication to sharing knowledge is unmistakable, and your writing style is captivating. Your articles are a pleasure to read, and I consistently come away feeling enriched. Thank you for being a dependable source of inspiration and information.
Your unique approach to addressing challenging subjects is like a breath of fresh air. Your articles stand out with their clarity and grace, making them a pure joy to read. Your blog has now become my go-to source for insightful content.
http://cialiskaufen.pro/# online-apotheken
http://viagrakaufen.store/# Viagra kaufen ohne Rezept legal
Hi there! Someone in my Myspace group shared this website with us so I came to look it over. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Terrific blog and excellent design and style.
http://cialiskaufen.pro/# versandapotheke deutschland
atorvastatin 10mg pill order atorvastatin 80mg pill brand lisinopril
Yay google is my queen aided me to find this outstanding site! .
https://mexicanpharmacy.cheap/# mexican rx online
oral duricef 500mg where can i buy combivir buy generic combivir online
In a world where trustworthy information is more important than ever, your commitment to research and providing reliable content is truly commendable. Your dedication to accuracy and transparency is evident in every post. Thank you for being a beacon of reliability in the online world.
I must commend your talent for simplifying complex topics. Your ability to convey intricate ideas in such a relatable way is admirable. You’ve made learning enjoyable and accessible for many, and I appreciate that.
I’ve discovered a treasure trove of knowledge in your blog. Your unwavering dedication to offering trustworthy information is truly commendable. Each visit leaves me more enlightened, and I deeply appreciate your consistent reliability.
http://mexicanpharmacy.cheap/# buying prescription drugs in mexico
purchase prilosec online buy lopressor tablets buy atenolol 50mg online